A therapeutic approach traditionally used for treating chronic pain is having a positive effect in treating asthma. In the study, “Neuromodulation for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Asthma — A Pilot First-in-Human Clinical Study,” researchers have detailed the surprising outcome of spinal cord stimulation (SCS) on patients with moderate to severe asthma. The study was recently published in the Journal of Asthma.
In a first-of-its-kind clinical trial, researchers implanted spinal cord stimulators in 11 patients suffering from both chronic pain and asthma. The results were striking: 91% of participants reduced their asthma medication use by more than 50%, and 73% eliminated medication use entirely within a year of treatment.
Additionally, all patients achieved well-controlled asthma, with an average improvement of 13.3 points and reported an improved quality of life, with an average increase of 3.4 points on the Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ). The study reported that there were no adverse events related to the use of the SCS device.
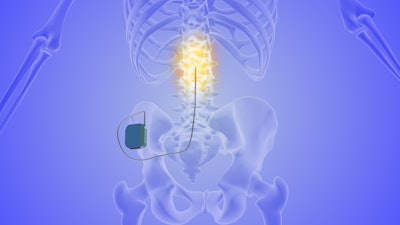
According to the study, the therapy involves implanting a spinal cord stimulator in the upper thoracic region, targeting neural pathways believed to contribute to asthma symptoms such as bronchoconstriction and mucus overproduction. By modulating these pathways, researchers said the device appears to reduce airway hyperresponsiveness without the need for traditional anti-inflammatory or bronchodilator medications.
Current asthma treatments often involve a cocktail of medications, including corticosteroids and biologics, which can be costly and come with side effects. This game-changing method for asthma control offers a drug-free, long-lasting solution, the study’s authors noted.
Although the results are promising, researchers noted the study’s small cohort and said it lacked a control group. Researchers are currently planning for a larger, randomized, multicenter trial to further evaluate the safety and efficacy of SCS in asthma patients. This future study will compare SCS to standard treatments, including biologics, and will use “clinical remission” as a primary endpoint.