Researchers have discovered that the process of attaching carbohydrates to proteins and lipids—or glycosylation—plays an intricate role in the pathogenesis of asthma. This is according to the new study, “Glycosylation in T2 high and Th17 Asthma: A Narrative Review,” which was published in the Journal of Asthma and Allergy and focuses on T2-high asthma and Th17-mediated responses.
Glycosylation, a post-translational modification, plays a crucial role in cellular signaling, protein stability and immune responses. The study examined how glycosylation affected airway inflammation, immune cell functionality and airway remodeling in asthma.
Key findings from the study include:
- Regulation of airway inflammation: Glycosylation modulates the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13, which are key components of T2 inflammation. It also influences the functionality of immune cells, including T cells and dendritic cells.
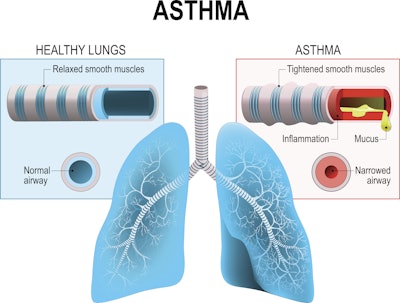
- Impact on airway remodeling: Glycosylation affects the proliferation and migration of airway smooth muscle cells, contributing to airway remodeling processes that exacerbate asthma symptoms.
- Molecular mechanisms: The study highlights various glycosylation modifications of proteins and genes implicated in asthma, such as IgE, IL-4 receptor and TGF-β. These modifications play a role in the regulation of immune responses and airway structural changes.
- Th17 cells and glycosylation: Th17 cells, which are involved in T2-high asthma, are also modulated by glycosylation. This adds another layer of complexity to the immune responses in asthma.
Additionally, researchers took note of:
- The role of macrophages: Macrophages play a crucial role in asthma by regulating airway inflammation, antigen presentation and immune responses. Glycosylation impacts macrophage function and activation through various mechanisms.
- Glycosylation in airway epithelial cells: Glycosylation of mucins like MUC5AC and MUC5B increases their viscosity and elasticity, leading to excessive mucus secretion and airway obstruction. Abnormal glycosylation of E-cadherin and TLR4 affects cell adhesion, barrier function and inflammatory responses.
- Glycosylation and other inflammatory mediators: Glycosylation’s status of leukotrienes, prostaglandins, histamine, TLRs and endothelin-1 influences their biological activity and interaction modes. This impacts airway inflammation, bronchoconstriction and mucus secretion.
According to researchers, the study underscores the potential of glycosylation in the development of therapeutic treatments for asthma. Discovering biomarkers and developing treatments that modulate glycosylation could lead to better management and prevention strategies for asthma.